前一段时间重构聊天服务的时候,需要定期去检测C端长连接的活跃情况,当检测到长链接失去心跳60s后,主动释放掉以节省内存开销。需要检测所有的长连接显然是不太明智的做法,因而想到了使用LRU算法,从最不活跃的连接检测,当检测到某个连接的活跃时间大于最近一分钟,后续的连接就无需检测了。
LRU(Least Recently Used)算法是一种常用的缓存淘汰策略算法,其核心思想是“如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高”。
package lru
import (
"container/list"
)
type Link struct {
ID int
ActiveTime int
}
type Lru struct {
maxSize int
list *list.List
cache map[*Link]*list.Element
}
func newLru(max int) *Lru {
return &Lru{
maxSize: max,
cache: map[*Link]*list.Element{},
list: list.New(),
}
}
func (l *Lru) Push(key *Link) {
if e, ok := l.cache[key]; ok {
l.list.MoveToFront(e)
} else {
row := l.list.PushFront(key)
l.cache[key] = row
}
for l.maxSize > 0 && l.list.Len() > l.maxSize {
l.removePassive()
}
}
func (l *Lru) CheckPassive() (*Link, bool) {
e := l.list.Back()
if e == nil {
return nil, false
}
link := e.Value.(*Link)
return link, true
}
func (l *Lru) Remove(key *Link) {
if e, ok := l.cache[key]; ok {
l.list.Remove(e)
delete(l.cache, key)
}
}
func (l *Lru) Len() int {
return l.list.Len()
}
func (l *Lru) removePassive() {
e := l.list.Back()
l.list.Remove(e)
delete(l.cache, e.Value.(*Link))
}
|
我们测试一下:
package lru
import "testing"
func TestLRU(t *testing.T) {
lru := newLru(10)
for i := 0; i < 20; i++ {
link1 := &Link{i, i + 1642262400}
lru.Push(link1)
}
old, _ := lru.CheckPassive()
t.Logf("CheckPassive:%+v", old)
t.Log("len=", lru.Len())
for true {
item, ok := lru.CheckPassive()
if !ok {
break
}
t.Logf("Remove:%+v", item)
lru.Remove(item)
}
old, _ = lru.CheckPassive()
t.Logf("CheckPassive:%+v", old)
t.Log("len=", lru.Len())
}
|
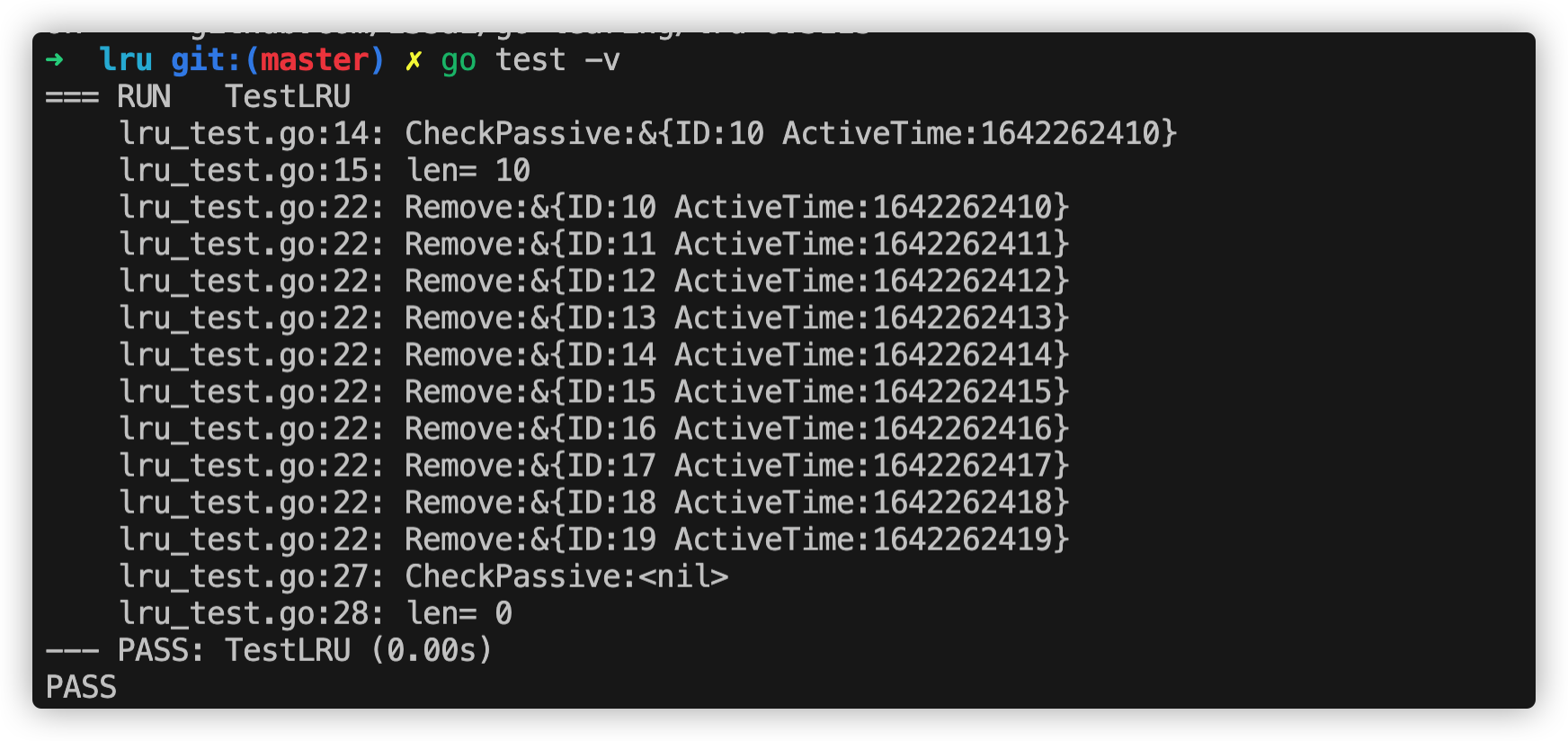
我们看一下输出:

看效果是ok的。别着急应用到项目中,记得压测对比下再实施哦!
参考: